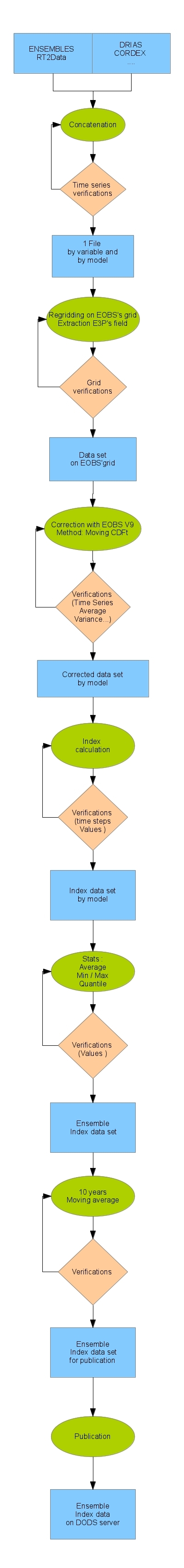
E3P is a European-funded project aiming at providing relevant climate indices for energy providers. In order to calculate these indices, we are using the ENSEMBLES, CORDEX, DRIAS and CMIP5 data bases.
This document describes the processing chain that allows transforming the raw data of these projects through the data correction by observations into relevant multi-models indices for energy providers.
To do so, the raw data goes through different steps:
This document describes the processing chain that allows transforming the raw data of these projects through the data correction by observations into relevant multi-models indices for energy providers.
To do so, the raw data goes through different steps: